Malvertising Campaign Hijacks Facebook Accounts to Spread SYS01stealer Malware
- November 4, 2024
- Posted by: claudia
- Categories:
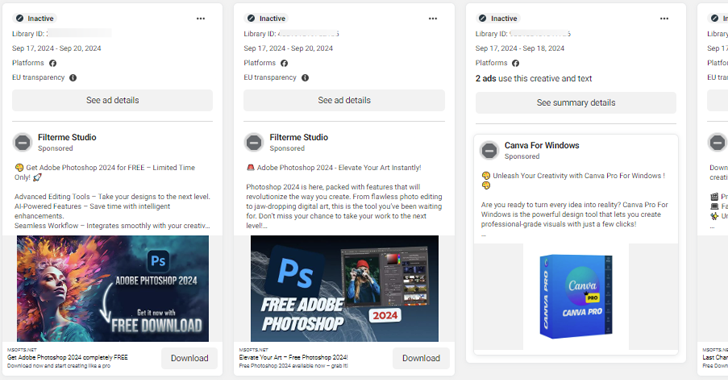
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a significant malvertising campaign exploiting Meta’s advertising platform. This campaign hijacks Facebook accounts to distribute a malware known as SYS01stealer. According to Bitdefender Labs, the attackers utilize trusted brands to enhance their reach and operate nearly one hundred malicious domains for both malware distribution and command/control operations, allowing real-time management of their attacks.
SYS01stealer was initially reported by Morphisec in early 2023, highlighting attack campaigns that specifically target Facebook business accounts through Google ads and fake profiles that promote varied content, including games and pirated software. The main objective of the malware is to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, browsing history, and cookies, with particular emphasis on extracting data from Facebook ad and business accounts, which further aids in the spread of malware via fraudulent advertisements.
The distribution of SYS01stealer predominantly occurs through malvertising on platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and LinkedIn. Targeting primarily males aged 45 and older, these advertisements promote various products, including Windows themes and VPN services, effectively enticing victims to click and inadvertently allowing their browser data to be compromised. Once a user interacts with an advertisement, they are redirected to deceptive sites designed to mimic legitimate brands, triggering the infection process.
The initial payload received from these malicious sites is a ZIP archive containing a benign executable that facilitates the loading of a malicious DLL. This DLL executes a multi-stage process, which includes running PowerShell commands to evade sandbox detection, modifying antivirus settings to bypass detection, and establishing an environment for operating the PHP-based stealer. Recent iterations of the malware incorporate an Electron application, indicating a continuous evolution of tactics among the threat actors.
The SYS01stealer campaign employs adaptive strategies, responding quickly to changes in cybersecurity defenses by updating the malware and pushing out new advertisements to avoid detection. In addition, if the malware detects it is being analyzed in a controlled environment, it suspends its operations to remain covert.
In a related development, Perception Point has outlined phishing campaigns abusing the Eventbrite platform to extract sensitive information from individuals. Attackers sign up for legitimate Eventbrite accounts, create fake events, and embed phishing links in event descriptions. These emails originate from a verified Eventbrite domain, enhancing their credibility and increasing the chances of passing through email filters, making recipients more likely to interact with the malicious links.
Moreover, a concerning trend has emerged in cryptocurrency fraud tactics reminiscent of ‘pig butchering’ schemes. Fraudsters impersonate various organizations to lure individuals with enticing job offers claiming substantial returns from home. This activity unfolds through social media, SMS, and messaging apps. Victims are instructed to register on malicious websites and complete tasks, often leading to financial exploitation when their supposed gains vanish, prompting them to invest more funds.
These fraudsters apply familiar brand recognition to enhance their schemes, providing a stark reminder that cybersecurity threats are continuously evolving. The interplay of phishing scams, malvertising, and cryptocurrency fraud underscores the need for vigilance and enhanced security measures among users to safeguard their personal and financial information.
