New Winos 4.0 Malware Infects Gamers Through Malicious Game Optimization Apps
- November 6, 2024
- Posted by: claudia
- Categories:
Cybersecurity experts have recently raised alarms regarding a sophisticated command-and-control (C&C) framework known as Winos, which is being disseminated through various gaming-related applications such as installation tools, speed boosters, and optimization utilities. According to a report from Fortinet FortiGuard Labs, Winos 4.0 is a highly advanced malicious framework that boasts a comprehensive set of functionalities, a robust architecture, and the capability to efficiently manage numerous online endpoints to execute additional actions. This framework is essentially a redesigned version of the Gh0st RAT and incorporates several modular elements, each designed for specific tasks.
The distribution of Winos 4.0 was initially identified in campaigns tracked by Trend Micro and the KnownSec 404 Team, which have classed the activity under the names Void Arachne and Silver Fox. These campaigns primarily target Chinese-speaking users through the use of black hat Search Engine Optimization (SEO) practices, as well as social media and messaging platforms like Telegram to spread the malware.
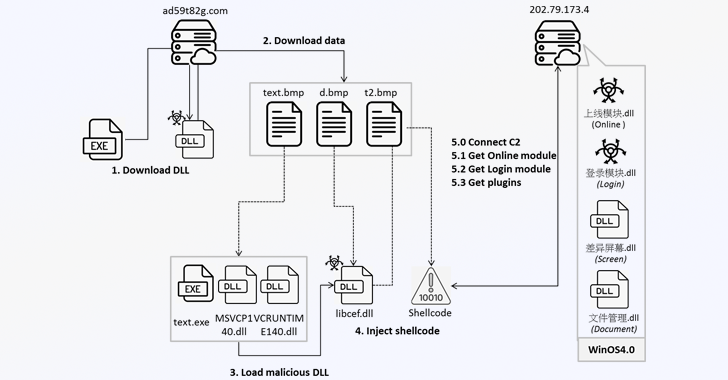
Fortinet’s analysis reveals that when users run the malicious gaming applications, they initiate a multi-stage infection process. This begins with the retrieval of a deceptive BMP file from a remote server, specifically “ad59t82g[.]com,” which is then decoded into a dynamic-link library (DLL). The initial DLL file is responsible for creating an execution environment by downloading three additional files from the same server, namely t3d.tmp, t4d.tmp, and t5d.tmp. The first two files are extracted to deliver subsequent payloads, which include an executable file (“u72kOdQ.exe”) and three other DLLs, one of which is named “libcef.dll.”
Notably, Fortinet highlighted that one of the DLLs, referred to as “学籍系统” (meaning “Student Registration System”), suggests a potential targeting of educational institutions by the threat actor. Following this, the malware utilizes the binary to load the “libcef.dll,” which extracts and runs second-stage shellcode from the t5d.tmp file. The malware establishes a connection with its command-and-control server (IP: “202.79.173[.]4”) through the TCP protocol, subsequently retrieving another DLL named “上线模块.dll.”
The third-stage DLL, integral to Winos 4.0, downloads encoded data from the C&C server, including a newly introduced DLL (“登录模块.dll”). This module is designed to gather detailed system information, capture clipboard data, collect information from cryptocurrency wallet extensions such as OKX Wallet and MetaMask, as well as maintain backdoor access by waiting for further commands from the C&C server.
Moreover, Winos 4.0 allows the deployment of additional plugins from the C&C server, enabling the malware to capture screenshots and exfiltrate sensitive documents from compromised systems. Fortinet characterized Winos 4.0 as a powerful and versatile framework, drawing parallels to other well-known tools like Cobalt Strike and Sliver, capable of performing multiple functions and executing comprehensive control over infected systems.
The strategic use of game-related applications as an approach to lure victims into unknowingly downloading and executing the malware underscores the increasing sophistication of cyberattack vectors, where malicious actors exploit popular platforms to evade user caution and successfully gain control over targeted devices.
