CERT-UA Identifies Malicious RDP Files in Latest Attack on Ukrainian Entities
- November 4, 2024
- Posted by: claudia
- Categories:
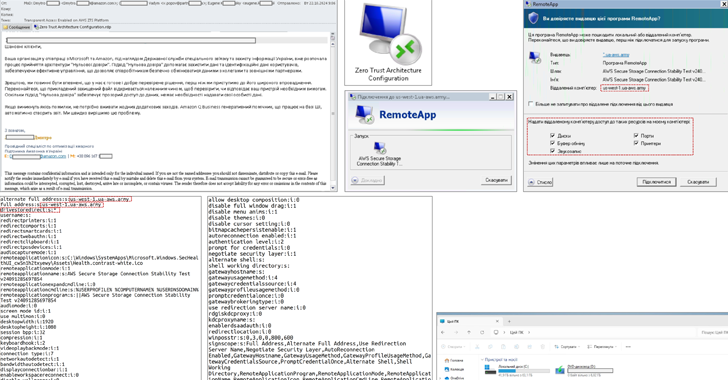
The Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) has issued warnings regarding a new and sophisticated email campaign spearheaded by a group identified as UAC-0215. This campaign is particularly directed at government institutions, military organizations, and enterprises, using cleverly crafted emails that suggest integration with widely-recognized services like Amazon and Microsoft, promoting the concept of zero-trust architectures. These emails contain attachments that are Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) configuration files, which, when executed, allow threat actors to connect with remote servers, facilitating unauthorized access to compromised systems, data theft, and the installation of additional malware.
The infrastructure for this operation purportedly began preparations as early as August 2024, raising concerns that its impact may extend beyond Ukraine’s borders to affect other nations. CERT-UA has linked the campaign to the Russian state-sponsored hacking group known as APT29, with Amazon Web Services (AWS) corroborating this attribution. AWS reported that the threats were not aimed at compromising AWS itself but rather targeted Windows credentials through Microsoft Remote Desktop. It further indicated that they have successfully taken control of domains used by the adversaries to impersonate AWS.
In conjunction with this threat, CERT-UA has also identified another cyberattack initiative labeled UAC-0218, which has a specific focus on the theft of confidential information belonging to Ukrainian users. This particular effort initiates through phishing emails containing links to compromised RAR archives disguised as invoices or payment notifications. Inside these archives resides malware, named HOMESTEEL, designed to exfiltrate files of various sensitive formats to servers controlled by the attackers.
Furthermore, CERT-UA highlighted a ClickFix-style campaign aiming to trick users into clicking malicious links embedded within email correspondence. This operation is engineered to deploy a PowerShell script capable of establishing an SSH tunnel, extracting data from users’ web browsers, and deploying the Metasploit penetration testing framework. Victims clicking these links are redirected to fraudulent reCAPTCHA verification pages, where they are misled into copying and executing malicious scripts on their machines. CERT-UA expressed a reasonable degree of confidence that this campaign is attributable to another Russian threat actor known as APT28.
These recent cyber assaults against Ukraine are part of a broader pattern observed in a report by Bloomberg, which discusses Russia’s military intelligence and FSB systematically targeting Georgia’s infrastructure and government entities from 2017 to 2020, with certain attacks associated with the Turla hacking group.
In a related vein, Microsoft released a report on October 29, 2024, affirming CERT-UA’s observations regarding APT29. Their findings indicated that this group has been actively sending tailored spear-phishing emails since October 22, targeting individuals across various sectors, including government and defense. Thousands of emails have been sent to over 100 organizations in countries such as the UK, Europe, Australia, and Japan, further emphasizing the global reach of the threat.
Microsoft’s analysis also revealed that APT29 employed RDP configuration files in their malicious emails, purportedly adding credibility by impersonating Microsoft staff and referencing other cloud service providers in their lures. Intelligence suggests that APT29 utilized email accounts from previous compromises, showcasing their methodical and persistent approach to cyber intrusions. The company stated it is in the process of notifying potentially affected customers and is offering support to help secure compromised accounts.
Moreover, new alerts have emerged from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), indicating that multiple sectors, especially government and IT, are currently experiencing a large-scale spear-phishing campaign. CISA stressed that foreign threat actors are masquerading as trusted entities, delivering spear-phishing emails with malicious RDP files aimed at accessing targeted organizations’ networks and files. Upon establishing access, these actors may proceed to deploy additional malicious software to maintain persistent control over the compromised networks.
In summary, the ongoing cyber threats against Ukraine and globally highlight an increasingly sophisticated landscape of cyber warfare. Both nation-state actors and advanced persistent threats are combining tactics to exploit the trust in established companies and services to facilitate broader malicious activities. The targeted nature of these operations underscores the importance of vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures within vulnerable sectors.
